Faraday Bags, named after the 19th-century scientist Michael Faraday, are specialized enclosures designed to block electromagnetic signals through the principle of the "Faraday cage"—a conductive barrier that traps electromagnetic fields, preventing signals from entering or exiting. In an era dominated by digital connectivity and growing concerns over data breaches, surveillance, and electromagnetic threats, these bags have evolved from niche tools to essential accessories for both professionals and everyday users. Below is a detailed exploration of their core functionalities, applications, design principles, and practical considerations.

I. Core Functionalities: Safeguarding in a Connected World1. Data Security and Cyber Protection: Shielding Against Digital Intrusions
In an age where remote hacking and data theft are rampant, Faraday bags serve as a physical barrier against unauthorized digital access. By blocking all electromagnetic signals—including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular (4G/5G), and NFC—they prevent bad actors from remotely infiltrating devices, stealing data, or altering information.

●Professional Use Cases:
(1)Journalists and investigative reporters rely on Faraday bags to protect sensitive sources, interview recordings, or confidential documents stored on laptops or phones, shielding them from state-sponsored surveillance or corporate espionage. For instance, during high-stakes investigations into corruption, a journalist can store their device in a Faraday bag to avoid being tracked or having their data remotely wiped.
(2)Corporate whistleblowers use them to secure internal documents or communication logs, ensuring that evidence of misconduct remains intact and unaltered.
Law enforcement and digital forensics teams depend on Faraday bags to preserve digital evidence. When seizing phones or laptops from crime scenes, these bags prevent suspects from remotely deleting data via hidden triggers or network commands, ensuring the evidence remains admissible in court.
Business travelers, especially those visiting regions with strict digital surveillance, use Faraday bags to protect proprietary data (e.g., client contracts, product blueprints) stored on devices, reducing the risk of theft during customs inspections or hotel stays.
●Everyday Relevance: Even casual users benefit—for example, storing a backup hard drive in a Faraday bag at home adds a layer of protection against ransomware attacks that might target connected devices.
2. Privacy and Anti-Tracking: Reclaiming Control Over Personal Data
In a world where location tracking and digital profiling have become ubiquitous, Faraday bags empower users to disconnect from unwanted monitoring. By isolating devices from external signals, they disrupt tracking mechanisms depend on GPS, Wi-Fi triangulation, or RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification).
Key Applications:
●Location Anonymity: Digital nomads, activists, or anyone seeking to avoid location monitoring can store their phones in Faraday bags to "go off the grid." This is particularly valuable in regions where governments or corporations engage in mass surveillance, as it prevents the logging of movement patterns.
●RFID Skimming Prevention:RFID chips embedded in passports, credit cards, and ID cards emit radio signals that can be intercepted by criminals using portable skimmers in crowded spaces (e.g., airports, public transit). Faraday sleeves or small pouches create a barrier, blocking these signals and preventing unauthorized access to personal information like credit card numbers or passport details.
●Preventing Unwanted Data Sharing:Smart devices (e.g., fitness trackers, smartwatches) often transmit data to manufacturers or third parties by default. Storing them in a Faraday bag when not in use halts this background data transfer, giving users greater control over their personal information.
3. Physical Security: Thwarting Theft and Unauthorized Access
Beyond digital threats, Faraday bags enhance physical security by protecting devices and valuables from theft-related exploitation.
●Automotive Security: Keyless entry systems in modern cars are vulnerable to "relay attacks," where criminals use two devices to amplify the signal from a car key fob (even when it’s inside a home), tricking the vehicle into unlocking. A Faraday pouch for key fobs blocks this signal, rendering such attacks ineffective—this simple solution has reduced keyless car theft by up to 60% in regions where it’s widely adopted.
●Theft Mitigation for Electronics: If a laptop or phone is stolen, a Faraday bag prevents the thief from accessing it remotely (e.g., via Find My Device) or tracking its location. For businesses, this adds a critical layer of protection for devices containing trade secrets or client data, minimizing the risk of data leakage post-theft.

4. EMF/EMP Protection: Guarding Against Energy and Radiation Threats
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) pose distinct risks to both devices and human health, and Faraday bags address both:
●EMP Shielding: EMPs—whether from natural sources (e.g., solar flares) or man-made (e.g., cyberattacks or nuclear detonations)—can fry electronic circuits, disabling critical devices like smartphones, generators, or emergency radios. Faraday bags act as a buffer, absorbing and dispersing the energy from EMPs, ensuring devices remain functional in disaster scenarios. This makes them a staple in emergency preparedness kits for households and organizations.
●EMF Radiation Reduction:Prolonged exposure to EMF radiation from devices (e.g., cell phones, Wi-Fi routers) has been linked to health issues such as headaches, fatigue, and disrupted sleep patterns, according to studies by the World Health Organization. Faraday bags limit this exposure by containing radiation within the enclosure; for example, storing a phone in a Faraday bag overnight reduces EMF exposure by over 99%, promoting healthier sleep environments.
II. Material and Design: Engineering Effective Shielding
The effectiveness of a Faraday bag hinges on its construction, which combines conductive materials and layered design to create an impenetrable barrier against signals.
Core Materials:
Conductive Metals: Copper and aluminum are the primary conductive layers, as they efficiently reflect and absorb electromagnetic waves. These metals are often woven into fabrics or laminated onto substrates to balance flexibility and shielding power.
Layered Shielding: Most Faraday bags use a multi-layer structure: an outer layer of durable, weatherproof material (e.g., nylon) for physical protection; a middle layer of conductive metal (copper or aluminum); and an inner layer of Mylar (a polyester film) to enhance signal blocking. This layering ensures no gaps in shielding, even with repeated use.
Performance Metrics:
●Signal Blocking Efficacy:Reputable Faraday bags are tested to block 100 dB or more of electromagnetic signals—this means they can nullify even the strongest cellular (5G), Wi-Fi (6E), and Bluetooth (5.3) signals, ensuring complete isolation.
●Durability: Designed for portability, they are lightweight (typically 200–500 grams) and resistant to water, tearing, and temperature extremes, making them suitable for outdoor use, travel, or industrial environments.
●User-Friendly Features:Many models include secure closures (e.g., double zippers with conductive lining to seal gaps), transparent windows (for device visibility without compromising shielding), and labeling for quick identification of device sizes.
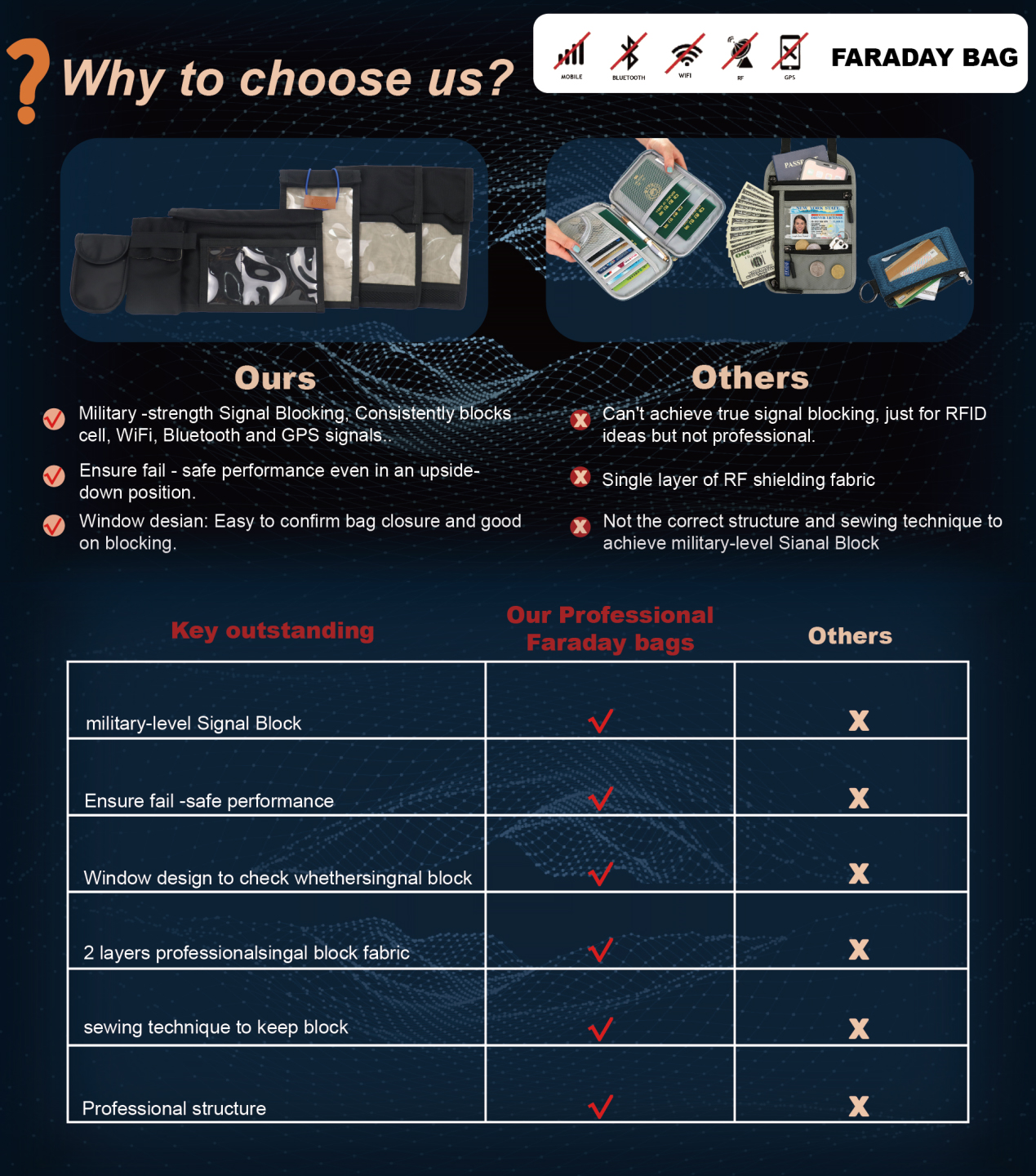
III. Versatility: Adapting to Diverse Devices and Needs
Faraday bags are not one-size-fits-all—they are engineered to accommodate a wide range of devices, ensuring protection for virtually any electronic item:
●Small Devices: Pouches for key fobs, credit cards, passports, and smartphones (e.g., iPhone 15 or Samsung Galaxy S24) are compact enough to fit in a pocket or purse, ideal for daily use.
●Medium Devices: Sleeves for tablets (e.g., iPad Pro) and e-readers protect larger screens while maintaining portability—popular among students and professionals who need occasional signal isolation.
●Large Devices: Bags for laptops (13–17 inches), drones, and even small appliances (e.g., smart speakers) are used by businesses and disaster preparedness enthusiasts to shield critical equipment.
●Custom Solutions: Industrial-grade Faraday bags are available for specialized gear, such as medical devices, military communication tools, or IoT sensors, ensuring compatibility with unique shapes and sizes.
IV. Practical Applications: From Professionals to Everyday Users
The utility of Faraday bags spans industries and lifestyles, with applications growing as digital threats evolve:
|
User Group |
Primary Use Case |
Example Benefit |
|
Journalists/Whistleblowers |
Protecting sources and sensitive data from surveillance. |
Prevents remote hacking of interview recordings during high-risk investigations. |
|
Law Enforcement |
Preserving digital evidence (e.g., phones, laptops) from tampering. |
Ensures data integrity for court cases by blocking remote wipes. |
|
Business Travelers |
Securing laptops and hard drives during international trips. |
Avoids data seizure or surveillance in regions with strict digital monitoring. |
|
Automotive Owners |
Shielding key fobs from relay attacks. |
Reduces keyless car theft by blocking signal amplification. |
|
Health-Conscious Users |
Reducing EMF exposure from phones and wearables. |
Improves sleep quality by limiting nighttime radiation from devices. |
|
Preppers/Disaster Teams |
Protecting emergency radios, generators, and communication devices from EMPs. |
Ensures functionality during solar flares or grid failures. |
V. Limitations and Considerations
While Faraday bags are highly effective, they are not without trade-offs, and users should weigh these factors before use:
●Signal Isolation Trade-Off:Devices inside a Faraday bag cannot receive calls, messages, or alerts—this is intentional for security, but it means users must plan for downtime (e.g., removing a phone to check urgent messages).
●Durability Over Time: Repeated opening and closing can wear down conductive linings, especially in low-quality bags. High-end models (e.g., those with reinforced zippers) maintain shielding effectiveness for 500+ uses, but budget options may degrade faster.
●Bulk vs. Portability:Larger bags for laptops or drones can be cumbersome to carry daily, making them better suited for occasional use (e.g., travel or storage) rather than constant transport.
●Cost: Quality matters—basic key fob pouches start at $10–$20, but professional-grade Laptop Bags can cost $50–$150. Investing in certified models (e.g., tested by the FCC or independent labs) ensures reliable performance.
VI. Future Trends: Innovations in Faraday Technology
As demand grows, manufacturers are refining Faraday bag design to address limitations:
●Smart Shielding: Some prototypes include "selective blocking," allowing users to disable specific signals (e.g., Wi-Fi) while permitting others (e.g., emergency calls), combining security with convenience.
●Sustainable Materials: Aimazingis experimenting with recycled conductive fabrics (e.g., reclaimed copper) to reduce environmental impact without sacrificing shielding power.
●Integration with Everyday Gear: Faraday liners built into backpacks, briefcases, or even clothing (e.g., jacket pockets) are emerging, making signal isolation seamless in daily life.

VII. Conclusion
Faraday bags have transitioned from technical curiosities to essential tools in the fight against digital threats, offering a tangible solution to intangible risks like hacking, surveillance, and electromagnetic interference. Whether used by a journalist protecting a source, a parent reducing their child’s EMF exposure, or a driver preventing car theft, these bags provide peace of mind in an increasingly connected world.
By understanding their functionality, choosing the right size for your devices, and weighing the trade-offs of signal isolation, you can leverage Faraday technology to safeguard both your data and your peace of mind. As digital threats continue to evolve, the role of Faraday bags in personal and professional security will only grow—making them a wise investment for anyone prioritizing privacy, safety, and device longevity.
Media Contact
Company Name: AIMAZING(Guangzhou) Co., Ltd.
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.aimazingbag.com/
